[SpringDB2] 데이터 접근 기술 - MyBatis 적용
MyBatis 적용1 - 기본
ItemMapper
@Mapper
public interface ItemMapper {
void save(Item item);
void update(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("updateParam") ItemUpdateDto updateParam);
Optional<Item> findById(Long id);
List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond itemSearch);
}
- MyBatis 매핑 XML을 호출해주는 Mapper 인터페이스이다.
- 이 인터페이스에는
@Mapper애노테이션을 붙여주어야 한다.- 그래야 MyBatis에서 인식할 수 있다.
- 이 인터페이스의 메서드를 호출하면 다음에 나오는
xml의 해당 SQL을 실행하고 결과를 돌려준다.
ItemMapper.xml
이제 같은 위치에 실행할 SQL이 있는 XML 매핑 파일을 만들어주면 된다.
참고로, 자바 코드가 아니기 때문에 src/main/resources하위에 만들되, 패키지 위치는 맞춰야 한다.
src/main/resources/hello/itemservice/repository/mybatis/ItemMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="hello.itemservice.repository.mybatis.ItemMapper">
<insert id="save" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into item (item_name, price, quantity)
values (#{itemName}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
<update id="update">
update item
set item_name=#{updateParam.itemName},
price=#{updateParam.price},
quantity=#{updateParam.quantity}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<select id="findById" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="findAll" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
<where>
<if test="itemName != null and itemName != ''">
and item_name like concat('%',#{itemName},'%')
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
and price <= #{maxPrice}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
namespace: 앞서 만든 매퍼 인터페이스를 지정하면 된다.
[참고] - XML 파일 경로 수정하기
XML 파일을 원하는 위치에 두고 싶으면application.properties에 다음과 같이 설정하면 된다.
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/**/*.xml
이렇게 하면 resources/mapper를 포함한 그 하위 폴더에 있는 XML을 XML 매핑 파일로 인식한다. 이 경우 파일 이름은 자유롭게 설정해도 된다.
insert - save
<insert id="save" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into item (item_name, price, quantity)
values (#{itemName}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
- Insert SQL은
를 사용하면 된다. id에는 매퍼 인터페이스에 설정한 메서드 이름을 지정하면 된다.- 파라미터는
#{}문법을 사용하면 된다. #{}문법을 사용하면PreparedStatement를 사용한다. JDBC의?를 치환한다 생각하면 된다.useGeneratedKeys는 데이터베이스가 키를 생성해 주는IDENTITY전략일 때 사용한다.keyProperty는 생성되는 키의 속성 이름을 지정한다. Insert가 끝나면item객체의id속성에 생성된 값이 입력된다.
update
void update(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("updateParam") ItemUpdateDto updateParam);
<update id="update">
update item
set item_name=#{updateParam.itemName},
price=#{updateParam.price},
quantity=#{updateParam.quantity}
where id = #{id}
</update>
- Update SQL은
<update>를 사용하면 된다. - 여기서는 파라미터가
Long id,ItemUpdateDto updateParam으로 2개이다. 파라미터가 1개만 있으면@Param을 지정하지 않아도 되지만, 파라미터가 2개 이상이면@Param으로 이름을 지정해서 파라미터를 구분해야 한다.
select - findById
<select id="findById" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
where id = #{id}
</select>
resultType은 반환 타입을 명시하면 된다. 여기서는 결과를Item객체에 매핑한다.- 앞서
application.properties에mybatis.type-aliases-package=hello.itemservice.domain속성을 지정한 덕분에 모든 패키지 명을 다 적지 않아도 된다. - JdbcTemplate의
BeanPropertyRowMapper처럼 SELECT SQL의 결과를 편리하게 객체로 바로 변환해준다. mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true속성을 지정한 덕분에 언터스코어를 카멜 표기법으로 자동으로 처리해준다.item_name->ItemName
- 앞서
- 자바 코드에서 반환 객체가 하나면
Item,Optional<Item>과 같이 사용하면 되고, 반환 객체가 하나 이상이면 컬렉션을 사용하면 된다.(주로List사용)
select - findAll
<select id="findAll" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
<where>
<if test="itemName != null and itemName != ''">
and item_name like concat('%',#{itemName},'%')
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
and price <= #{maxPrice}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- MyBatis는
<where>,<if>같은 동적 쿼리 문법을 통해 편리한 동적 쿼리를 지원한다. <where>은 적절하게where문장을 만들어준다.<if>가 모두 실패하게 되면 SQLwhere를 만들지 않는다.<if>가 하나라도 성공하면 처음 나타나는and를where로 변환해준다.
XML 특수 문자
and price <= #{maxPrice}를 보면 XML에서는 데이터 영역에 <, >같은 특수 문자를 사용할 수 없기 때문에 대체해서 사용했다.
다른 해결 방안으로는 XML에서 지원하는 CDATA 구문 문법을 사용하는 것이다. 이 구문 안에서는 특수 문자를 사용할 수 있다. 대신 이 구문 안에서는 XML TAG가 단순 문자로 인식되기 때문에 <if>, <where>등이 적용되지 않는다.
XML CDATA 사용
<select id="findAll" resultType="Item">
select id, item_name, price, quantity
from item
<where>
<if test="itemName != null and itemName != ''">
and item_name like concat('%',#{itemName},'%')
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
<![CDATA[
and price <= #{maxPrice}
]]>
</if>
</where>
</select>
MyBatis 적용2 - 설정과 실행
MyBatisItemRepository
@Repository
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MyBatisItemRepository implements ItemRepository {
private final ItemMapper itemMapper;
@Override
public Item save(Item item) {
itemMapper.save(item);
return item;
}
@Override
public void update(Long itemId, ItemUpdateDto updateParam) {
itemMapper.update(itemId, updateParam);
}
@Override
public Optional<Item> findById(Long id) {
return itemMapper.findById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Item> findAll(ItemSearchCond cond) {
return itemMapper.findAll(cond);
}
}
MyBatisItemRepository는 단순히ItemMapper에 기능을 위임한다.
MyBatisConfig
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MyBatisConfig {
private final ItemMapper itemMapper;
@Bean
public ItemService itemService() {
return new ItemServiceV1(itemRepository());
}
@Bean
public ItemRepository itemRepository() {
return new MyBatisItemRepository(itemMapper);
}
}
MyBatisConfig는ItemMapper를 주입받고, 필요한 의존관계를 만든다.
MyBatis 적용3 - 분석
ItemMapper인터페이스는 구현체가 없는데 어떻게 동작하는 것인가?
이 부분은 MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈에서 자동으로 처리해준다.
설정 원리
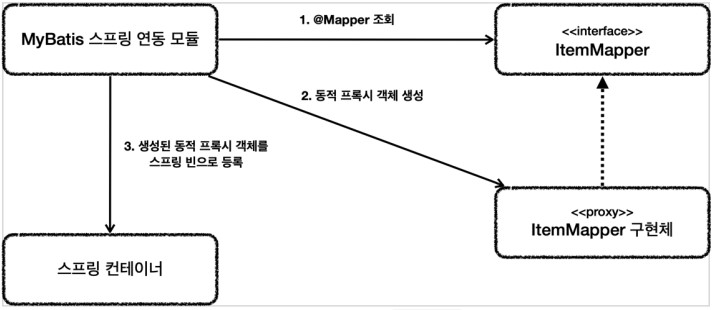
- 애플리케이션 로딩 시점에 MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈은
@Mapper가 붙어있는 인터페이스를 조사한다. - 해당 인터페이스가 발견되면 동적 프록시 기술을 사용해서
ItemMapper인터페이스의 구현체를 만든다. - 생성된 구현체를 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
매퍼 구현체
- MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈이 만들어주는
ItemMapper의 구현체 덕분에 인터페이스 만으로 편리하게 XML의 데이터를 찾아서 호출할 수 있다. - 매퍼 구현체는 예외 변환까지 처리해준다.
- MyBatis에서 발생한 예외를 스프링 예외 추상화인
DataAccessException에 맞게 변환해서 반환해준다. JdbcTemplate이 제공하는 예외 변환 기능을 여기서도 제공한다고 보면 된다.
- MyBatis에서 발생한 예외를 스프링 예외 추상화인
정리
- 매퍼 구현체 덕분에 MyBatis를 스프링에 편리하게 통합해서 사용할 수 있다.
- 매퍼 구현체를 사용하면 스프링 예외 추상화도 함께 적용된다.
- MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈이 많은 부분을 자동으로 설정해 주는데, 데이터베이스 커넥션, 트랜잭션과 관련된 기능도 MyBatis와 함께 연동하고, 동기화해준다.
[참고]
MyBatis 스프링 연동 모듈이 자동으로 등록해주는 부분은MybatisAutoConfiguration클래스를 참고.
MyBatis 기능 정리1 - 동적 쿼리
동적 SQL
MyBatis를 사용하는 이유는 MyBatis가 제공하는 동적 SQL 기능 때문이다.
ifchoose (when, otherwise)trim (where, set)foreach
if
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
</select>
- 해당 조건에 따라 값을 추가할지 말지 판단한다.
choose, when, otherwise
<select id="findActiveBlogLike" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
- 자바의 switch 구문과 유사한 구문도 사용할 수 있다.
foreach
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT * FROM POST P
<where>
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="ID in (" separator="," close=")" nullable="true"> #{item}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
- 컬렉션을 반복 처리할 때 사용한다.
where in (1,2,3,4,5,6)와 같은 문장을 쉽게 완성할 수 있다.
- 파라미터로
List를 전달하면 된다.
MyBatis 기능 정리2 - 기타 기능
애노테이션으로 SQL 작성
@Select("select id, item_name, price, quantity from item where id = #{id}")
Optional<Item> findById(Long id);
@Insert,@Update,@Delete,@Select기능이 제공된다.- 이 경우 XML에 작성한
select코드는 제거해야 한다.- 충돌 문제 발생..
- 동적 SQL이 해결되지 않으므로 간단한 경우에만 사용한다.
문자열 대체
#{} 문법은 ?를 넣고 파라미터를 바인딩하는 PreparedStatement를 사용한다.
파라미터 바인딩이 아니라 문자 그대로를 처리하고 싶은 경우에는 ${}를 사용하면 된다.
@Select("select * from user where ${column} = #{value}")
User findByColumn(@Param("column") String column, @Param("value") String value);
주의!
${}를 사용하면 SQL 인젝션 공격을 당할 수 있기 때문에, 가급적 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다.
Result Maps
결과를 매핑할 때 테이블은 user_id이지만 객체는 id라면?
이 경우 컬럼명과 객체의 프로퍼티 명이 다르기 때문에 별칭(as)을 사용해도 되고, 별칭을 사용하지 않고 해결하려면 resultMap을 선언해서 사용하면 된다.
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="User">
<id property="id" column="user_id" />
<result property="username" column="user_name"/>
<result property="password" column="password"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUsers" resultMap="userResultMap">
select user_id, user_name, hashed_password
from some_table
where id = #{id}
</select>
댓글남기기