[Spring MVC] HTTP 메시지 컨버터
HTTP 메시지 컨버터
HTTP API처럼 JSON 데이터를 HTTP 메시지 바디에서 직접 읽거나 쓰는 경우 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 사용하면 편리하다.
@ResponseBody 사용 원리
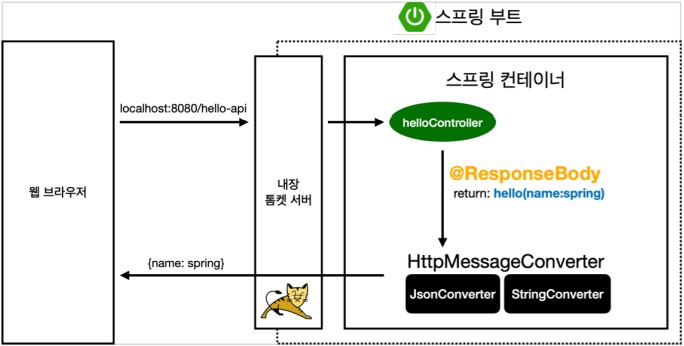
@ResponseBody사용- HTTP Body의 문자 내용을 직접 반환
viewResolver대신에HttpMessageConverter가 동작- 기본 문자처리:
StringHttpMessageConverter - 기본 객체처리:
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
스프링 MVC는 다음 경우에 HttpMessageConverter를 적용한다.
- HTTP 요청:
@RequestBody,HttpEntity(RequestEntity) - HTTP 응답:
@ResponseBody,HttpEntity(ResponseEntity)
HttpMessageConverter 인터페이스
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
void write(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage
outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
}
HttpMessageConverter는 HTTP 요청, 응답 둘 다 사용된다.
canRead(),canWrite(): 메시지 컨버터가 해당 클래스, 미디어타입을 지원하는지 체크read(),write(): 메시지 컨버터를 통해서 메시지를 읽고 쓰는 기능
스프링 부트 기본 메시지 컨버터
(일부 생략…)
0 = ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter
1 = StringHttpMessageConverter
2 = MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
대상 클래스 타입과 미디어 타입 둘을 체크해서 사용여부를 결정한다.
ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter:byte[]데이터를 처리한다.- 클래스 타입:
byte[], 미디어타입:*/* - 요청 Ex)
@RequestBody byte[] data - 응답 Ex)
@ResponseBody return byte[], 쓰기 미디어타입application/octet-stream
- 클래스 타입:
StringHttpMessageConverter:String문자로 데이터를 처리한다.- 클래스 타입:
String, 미디어타입:*/* - 요청 Ex)
@RequestBody String data - 응답 Ex)
@ResponseBody return "ok", 쓰기 미디어타입text/plain
- 클래스 타입:
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter:application/json- 클래스 타입: 객체 또는
HashMap, 미디어타입application/json관련 - 요청 Ex)
@RequestBody HelloData data - 응답 Ex)
@ResponseBody return helloData, 쓰기 미디어타입application/json관련
- 클래스 타입: 객체 또는
StringHttpMessageConverter
content-type: application/json
@RequestMapping
void hello(@RequestBody String data) {}
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
content-type: application/json
@RequestMapping
void hello(@RequestBody HelloData data) {}
HTTP 요청 데이터 읽기
- HTTP 요청이 오고, 컨트롤러에서
@RequestBody,HttpEntity파라미터를 사용한다. - 메시지 컨버터가 메시지를 읽을 수 있는지 확인하기 위해
canRead()를 호출.- 대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는가?
- Ex)
@RequestBody의 대상 클래스(byte[],String,HelloData)
- Ex)
- HTTP 요청의 Content-Type 미디어 타입을 지원하는가?
- Ex)
text/plain,application/json,*/*
- Ex)
- 대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는가?
canRead()조건을 만족하면read()를 호출해서 객체 생성 후 반환.
HTTP 응답 데이터 생성
- 컨트롤러에서
@ResponseBody,HttpEntity로 값이 반환. - 메시지 컨버터가 메시지를 쓸 수 있는지 확인하기 위해
canWrite()호출.- 대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는가?
- Ex) return의 대상 클래스(
byte[],String,HelloData)
- Ex) return의 대상 클래스(
- HTTP 요청의 Accept 미디어 타입을 지원하는가?(
@RequestMapping-produces)- Ex)
text/plain,application/json,*/*
- Ex)
- 대상 클래스 타입을 지원하는가?
canWrite()조건을 만족하면write()를 호출해서 HTTP 응답 메시지 바디에 데이터 생성.
요청 매핑 핸들러 어뎁터 구조
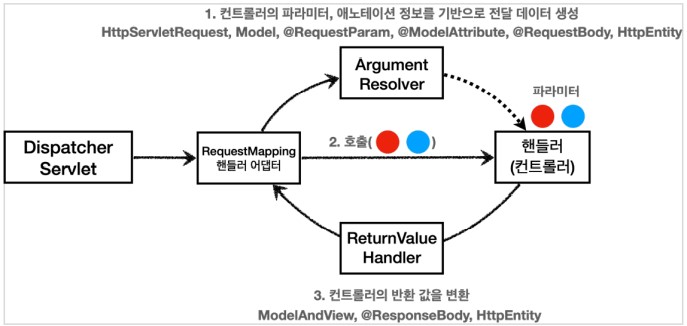
ArgumentResolver
애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러는 HttpServletRequest, Model / @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute같은 애노테이션 그리고 @ReqeustBody, HttpEntity같은 HTTP 메시지를 처리하는 부분까지 큰 유연함을 보인다.
이렇게 파라미터를 유연하게 처리할 수 있는 이유가 ArgumentResolver 덕분이다.
애노테이션 기반 컨트롤러를 처리하는 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter는 ArgumentResolver를 호출해서 핸들러가 필요로 하는 다양한 파리미터의 값(객체)를 생성한다.
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
@Nullable
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter,
@Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest,
@Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory
) throws Exception;
}
동작
ArgumentResolver의 supportsParameter()를 호출해서 해당 파라미터를 지원하는지 체크하고, 지원하면 resolveArgument()를 호출해서 실제 객체를 생성한다.
이렇게 생성된 객체가 컨트롤러 호출시 넘어간다.
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
ArgumentResolver와 비슷하지만, 응답 값을 변환하고 처리한다.
Ex) ModelAndView, @ResponseBody, HttpEntity, String
컨트롤러에서 String으로 뷰 이름을 반환해도 동작하는 것이 ReturnValueHandler 덕분이다.
HTTP 메시지 컨버터 구조
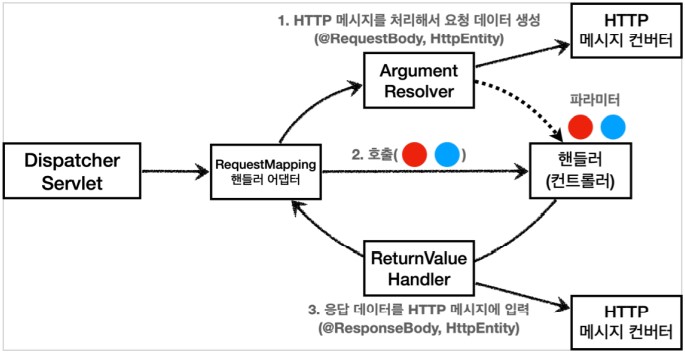
요청의 경우 @ReuqestBody, HttpEntity를 처리하는 ArgumentResolver가 있다. ArgumentResolver들이 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 사용해서 필요한 객체를 생성한다.
응답의 경우 @ResponseBody와 HttpEntity를 처리하는 ReturnValueHandler가 있다. 여기에서 HTTP 메시지 컨버터를 호출해서 응답 결과를 만든다.
스프링 MVC는 @RequestBody, @ResponseBody가 있으면 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor(ArgumentResolver)
HttpEntity가 있으면 HttpEntityMethodProcessor(ArgumentResolver)를 사용.
확장 스프링은 다음을 모두 인터페이스로 제공한다. 따라서 필요하면 언제든지 기능을 확장할 수 있다.
HandlerMethodArgumentResolverHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerHttpMessageConverter
댓글남기기